Symptoms
- Spinning, swaying, or tilting sensations
- Feeling unsteady or imbalanced
- Dizziness or a falling sensation
- Difficulty focusing on moving objects
- Nausea
- Changes in hearing or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Difficulty concentrating

Vertigo is a false sensation of motion, often described as spinning, imbalance, or feeling light-headed. It is commonly associated with symptoms like nausea, vomiting, or unsteadiness while walking. Vertigo can worsen when you move your head. It is important to differentiate vertigo from acrophobia (fear of heights).
Vertigo and dizziness are common complaints that affect people of all ages. Studies show that 20-40% of individuals will experience dizziness at some point in their lives. In any given year, 5% of people will experience vertigo, and 2.5% of primary care visits in the developed world are related to vertigo.
It’s crucial to understand that vertigo is not a disease in itself but a symptom of an underlying disorder. Proper diagnosis of the cause is key to appropriate treatment.
Since vertigo is a symptom, it is essential to identify the underlying cause through diagnostic tests like Video Nystagmography (VNG) for accurate treatment.
Medications are typically prescribed to manage dizziness and the associated discomfort, such as nausea, vomiting, fatigue, anxiety, and visual disturbances. Drugs like Vertin, Stugeron, Meclizine Hydrochloride, and Stemetil are often used. However, prolonged use of these medications is not recommended, as they can be harmful and should not be taken for more than 5 days.
Surgery is usually reserved for rare cases of vestibular disorders, as inner ear surgeries can be complex.
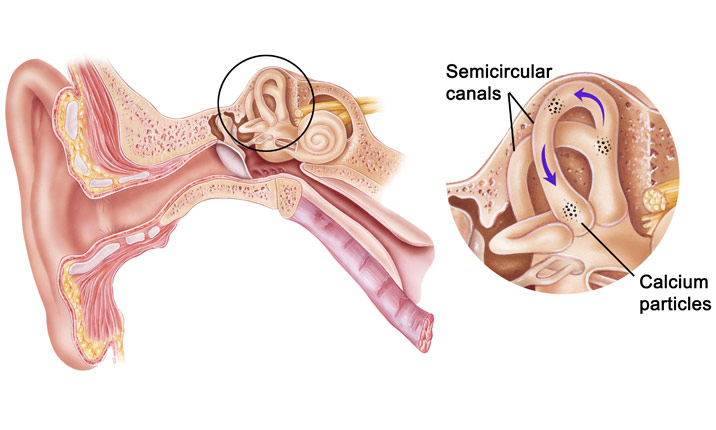
Vestibular rehabilitation exercises and canalith repositioning maneuvers are helpful in managing certain vestibular disorders. These therapies are effective for improving balance, reducing dizziness, and normalizing visual disturbances. Canalith repositioning maneuvers (such as Epley, Semont, or Barbeque maneuvers) are particularly helpful for patients with BPPV.
Some useful tips to avoid or manage vertigo include: