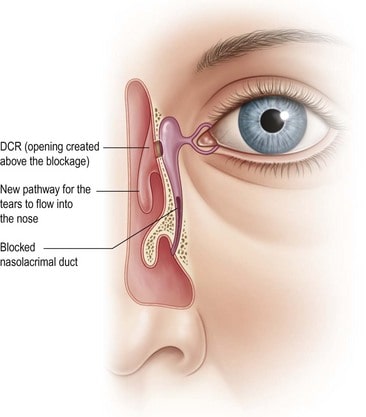
A dacrocystorhinostomy (DCR) is a surgical procedure used to address excessive tear flow, also known as epiphora, resulting from a blockage in the nasolacrimal duct. Tears typically follow a lengthy path from the eye's opening in the eyelids to the lacrimal sac (located between the nose and the eye) and eventually through the nasolacrimal duct (tear duct) into the nasal cavity. Any obstruction along this route can lead to increased tear outflow, and one common cause is a blocked nasolacrimal duct. DCR surgery establishes a direct connection between the lacrimal sac and the nasal cavity, creating a direct drainage route. While there are identifiable factors such as trauma, prior surgery, tumors, or inflammatory medical conditions that can cause this duct blockage, in many cases, determining the exact underlying cause can be challenging.
The evaluation and management of a DCR procedure may involve both an ophthalmologist and an otolaryngologist.