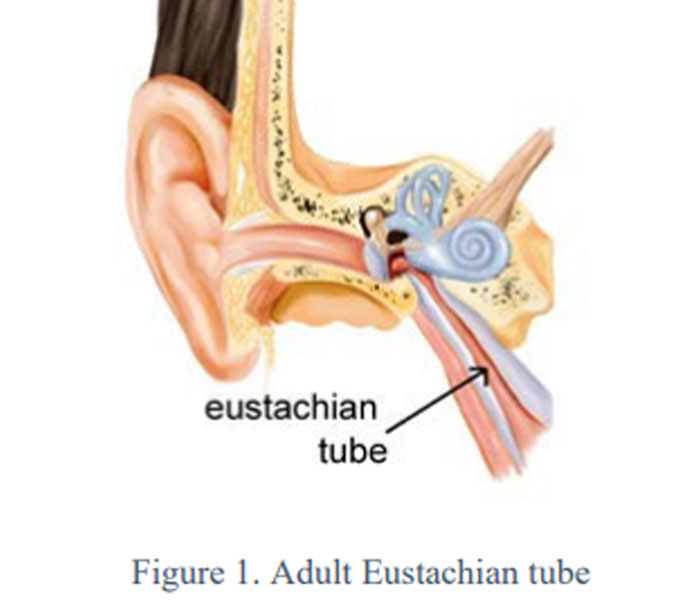
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) is characterized by a blockage or impaired opening of the Eustachian Tube.
It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional if you suspect you have Eustachian tube dysfunction, as they can determine the underlying cause and recommend the most appropriate treatment. Untreated ETD can lead to more serious complications, including chronic ear infections or hearing loss.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD) can be caused by various conditions, and its manifestations can range from mild to severe.
If you suspect Eustachian Tube Dysfunction or are experiencing related symptoms, it's advisable to seek medical attention for a proper evaluation and guidance on appropriate management.
1. Utilizing decongestant sprays to alleviate tube swelling is a common approach
2.If ETD stems from allergies, antihistamines are advised to mitigate allergic reactions.
1. Eustachian Tube Balloon Dilation involves the inflation of a small balloon into the Eustachian tube through the nasal passage, facilitating the clearance of mucus and air flow. For further details, please click here (link redirects to the surgery page).
2.Myringotomy entails a minor incision made by the ENT surgeon in the eardrum, allowing for the removal of any fluid within the middle ear through suction. Additionally, a small, hollow pressure equalization tube may be inserted, providing ventilation to the middle ear for a period of 6-12 months.